This chapter explains how to do link design. Click Link Engineering to view the list of Active Link Engineering Designs. Manual design page is shown as follows:
Figure 60: 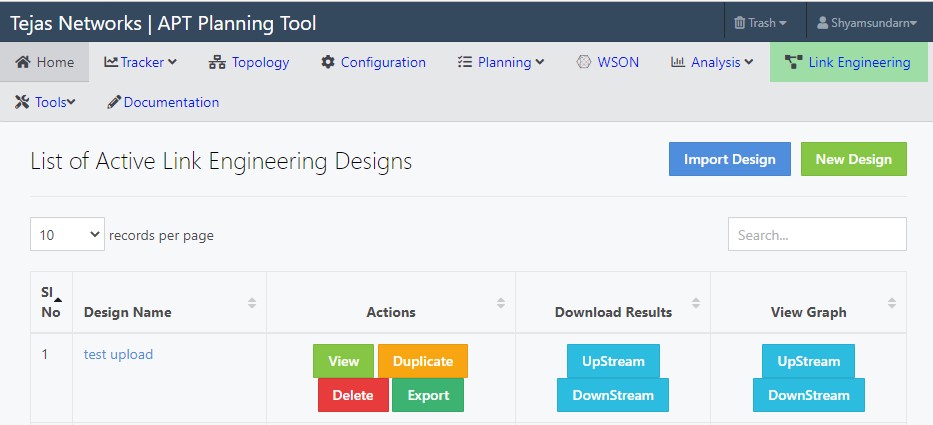 Manual link design page
Manual link design page
This section describes about available buttons. Following are the available buttons:
— New Design: Click New Design button to add new design.
— Import Design: Click Import Design button to import an existing design.
8.2 List of available link engineering designs
A table with following columns are displayed as follows:
1. Sl No: Serial number is used to enumerate the available link designs.
2. Design Name: Displays the name of the design.
3. Actions: This column has maximum four buttons as follows:
— View: To view the design click View.
— Duplicate: To duplicate the design click Duplicate.
— Delete: To delete the design click Delete.
— Export: To export the design click Export.
4. Download Results: This column has following two buttons:
— UpStream: To download the UpStream simulation results in excel file, click the UpStream button.
— DownStream: To download the DownStream simulation results in excel file, click the DownStream button.
5. View Graph: This column has following two buttons:
— UpStream: To view the UpStream OSNR reports, click UpStream button.
— DownStream: To view DownStream OSNR reports, click DownStream button.
NOTE: Depending on the situation, UpStream and DownStream buttons may not be visible.
This section describes how to create new link design. To create a new design, click New Design button which is available at the top-right corner and the form appears. Following are the available parameters:
1. Name of the Design: Provide name of the link engineering design.
2. Select the Project: Select the desired project from the drop-down list
3. Max no of Wavelength in Each Fiber: Select the Max no of Wavelength in Each Fiber from the drop-down. There are two types of Max no of Wavelength in Each Fiber:
— 96 Wavelength Network
— 40 Wavelength Network
4. Design Type: Select the design type from the following:
— Fix Grid 50G
— Fix Grid 100G odd channels
— Fix Grid 100G even channels
5. Loss Margin: Provide the Loss Margin (dB) value.
6. After filling the form, click Submit to save the design.
8.2.2 Add data to upstream or downstream of design
This section describes how to add data to upstream or downstream of design. To view the existing design, click View button to view a particular network design. If you select test network from the list of available link engineering design, it redirects to new page which has both upstream and downstream design.
8.2.2.1 Available sections
Between any two nodes, there are two paths for traffic. One path is labeled as downstream and another as upstream. Following are the two available sections which discusses about downstream and upstream traffics respectively:
1. Downstream: Source and destination node provided by the user in the form are as associated, as a convention, with the downstream traffic.
2. Upstream: Upstream traffic by convention has source node and destination node exchanged to what is provided by the user, meaning the source node of the downstream traffic becomes destination node for the upstream traffic and the destination node of the downstream traffic becomes source node for the same upstream traffic.
8.2.2.2 Available buttons
Following are the available buttons:
1. Replicate to Downstream: To replicate upstream components to downstream click Replicate to Downstream which is available at the top-right corner.
2. Update: To update and to run simulation click Update button which is available at the top-right corner. Click Update button to add or modify upstream or downstream components with in the upstream or downstream page.
NOTE: Replication function cannot perform complete replication of all components with parameters, it is recommended to check before running simulation for downstream.
8.2.2.3 Steps to add or modify any design
This section describes steps to modify or update any design. Click Update button available at the top-right corner.
Following are the nine columns:
1. Node Name: Add node name properly to distinct components of different nodes and click node name by clicking left mouse button in the displayed list to modify the node name.
2. Component Type: Currently the following components are supported:
— Line card: It is an electrical device from which data traffic originates through lasers.
— MDU: With this device with this device we can either multiplex the optical signal or demultiplex based on source and destination.
— ROADM: It is an optical device and stands for Reconfigurable Optical Add and Drop Module.
— Fiber: This is the medium through which the optical signal travels from source to destination.
— Attenuator: This device is used for attenuating the signal power.
— OFA: EDFA Amplifier used for amplifying the signal strength.
— ORA: RAMAN Amplifier used in special cases or when there is high link loss.
— DCM/DCU: It is an optical device and stands for Dispersion Compensation Module/Unit.
— PSCM: It is an optical device and stands for Power Splitter and Combiner Module. Splitter splits the power into multiple parts depending the device type. Combiner combines multiple powers into one.
— OSCF: Optical supervisory channel
— Coupler: It is an optical device used for splitting and combining C-band and L-band channels
— FPU: It is an optical device and stands for Fiber Protection Unit.
3. Component Name: After selecting the Component Type, application shows the available components based on configuration such as number of lambda per fiber.
NOTE: For 80 channels design, ILU is not shown as independent component but show along with MDU as MDU40E-MDU40O-ILU component (if there are 40 even channels MDU and 40 odd channels MDU, then ILU is used to combine channels).
4. Direction Each component type takes different directions as follows:
— Line card add and drop direction
— MDU add and drop direction
— ROADM add and drop direction
— Fiber Only add direction
— PSCM Only add direction
— Attenuator only add direction
— OFA Only add direction
— ORA Only add direction
— DCM Only add direction
— DCU Only add direction
— OSC Only add direction
— Coupler add and drop direction
— FPU add and drop direction
5. Device Loss: As soon as we click on Device Loss, tool takes default loss value of mentioned device, otherwise enter the device loss accordingly.
6. Parameter 1: Click Parameter1 with left mouse button with respect for each component type. Each component type takes different parameters:
— Line Card: For add direction select the data rate, channel, enable FEC and enter valid channel power.
Figure 61:  Linecard configuration for manual link design
Linecard configuration for manual link design
— MDU: For add direction, select the channel.
Figure 62: Manual link design MDU details
— MDU: For drop direction, select the channel.
— ROADM: For add direction, select the channel and provide channel power. Balanced power and attenuation are taken care by the APT application. If power equalization required, then select Auto Power Equalization. The Auto power Equalization button makes booster amplifier all the channels output power to be equal if only VG/LVG amplifier is used as booster and also it compensates the tilt only if it is given according to fiber tilt calculation that is, -0.0085 dB per Km). For drop direction select the channel. If any channel is a pass through channel for a starting node then directly add it as add channel at add ROADM of starting node. Similarly, make a channel as pass through channel at add ROADM of the end node (If channel is not terminating at end node).
» Fiber: Provide distance value (km)
» Attenuator: Provide the loss value (dB)
» OFA: Provide gain value (dB)
» ORA: Provide gain value (dB)
7. Parameter 2: Only applicable for Fiber and Variable Gain amplifier types.
NOTE 1: Component Parameter 2 for fiber takes only measured loss.
NOTE 2: Component Parameter 2 for OFA Variable Gain amplifiers take tilt values between -2 and 2.
NOTE 3: Application finds the wrong configuration and warns the user. All the configurations checks are not verified by the application. If some configuration is not allowed, please consider it as limitation. Fiber G.652 is considered and dispersion 17 ps/nm-km. It can be changed in the design parameters.
8. Enable: Enable or Disable the component from the design simulation by clicking it. Once all the components are added, click Save which is available at the top-right corner.
9. Click Validate to validate the design which is available at the top-right corner and application will return the design results. Even after saving and validating the design, user can edit the network, save and validate the same.
10. Click Schedule Validation to validate the design using tasks which is available at the top-right corner. Application will store the design results and you can download it on the main page.
NOTE: All the component simulations are verified against practical component performance.
After validating the design, application gives the OSNR report as shown in the figure. The figure explains that when services flow through a link, they pass through multiple devices and certain loss occurs because of which OSNR degrades.
Figure 63: Manual link design simulation 
1. If you want to download the complete simulation results in excel file, then click Download Result button available at the center of the screen to download the file. File has each component optical parameters such as Input Power, Output Power, Input OSNR, Output OSNR, Input Dispersion, and Output Dispersion for each lambda.
2. Run simulation for upstream and downstream separately.
NOTE: Manual Link Design is independent of network system design. The networks which are designed by APT cannot be modified.
3. Download each optical parameter separately in pdf, png, jpg and SVG image format by clicking on chart context menu available the right corner of the screen as shown in the figure.
Figure 64: Manual link simulation 
To delete the design, click Delete button of the corresponding design from the list in the table.
1. Click Link Engineering Design button from Trash menu to access list of all deleted Link Engineering Designs.
2. To restore deleted link design, click Restore button; pop-up appears asking confirmation on restore action, if the link design is to be restored, then click OK.
3. Corresponding link design gets restored. If there is no need to restore link design, then click Cancel button. Corresponding link design does not get restored.
Figure 65: Design page showing list of all deleted link designs
To duplicate the design, click Duplicate button of the corresponding design from the list in the table.
To export the design, click Export button of the corresponding design from the list in the table and save it as an .xml file.
To import the design, click Import button and add the file. File should be in.xml format.