The Class of Service (CoS) queueing feature lets you directly configure certain aspects of switch queuing. This provides the desired QoS behavior for different types of network traffic when the complexities of DiffServ are not required. The priority of a packet arriving at an interface can be used to steer the packet to the appropriate outbound CoS queue through a mapping table. CoS queue characteristics that affect queue mapping, such as minimum guaranteed bandwidth, transmission rate shaping, etc., are user-configurable at the queue (or port) level.
Seven queues per port are supported. Although the hardware supports eight queues, one queue is always reserved for internal use by the stacking subsystem.
Use the Trust Mode Configuration page to set the class of service trust mode of an interface. Each port in the switch can be configured to trust one of the packet fields (802.1p or IP DSCP), or to not trust any packet’s priority designation (untrusted mode). If the port is set to a trusted mode, it uses a mapping table appropriate for the trusted field being used. This mapping table indicates the CoS queue to which the packet should be forwarded on the appropriate egress port(s). Of course, the trusted field must exist in the packet for the mapping table to be of any use, so there are default actions performed when this is not the case. These actions involve directing the packet to a specific CoS level configured for the ingress port as a whole, based on the existing port default priority as mapped to a traffic class by the current 802.1p mapping table.
Alternatively, when a port is configured as untrusted, it does not trust any incoming packet priority designation and uses the port default priority value instead. All packets arriving at the ingress of an untrusted port are directed to a specific CoS queue on the appropriate egress port(s), in accordance with the configured default priority of the ingress port. This process is also used for cases where a trusted port mapping is unable to be honored, such as when a non-IP packet arrives at a port configured to trust the IP precedence or IP DSCP value.
To display the Trust Mode Configuration page, click Quality of Service > Class of Service > Trust Mode Configuration in the navigation menu.
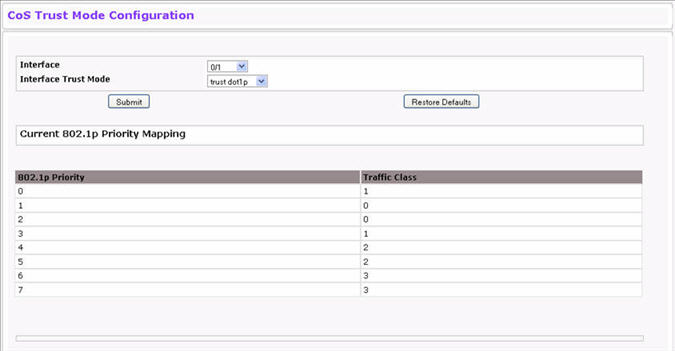
Trust Mode Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface/Global |
The menu contains all CoS configurable interfaces. Select the Global option to apply the same trust mode to all interfaces. Select an individual interface from the menu to override the global settings on a per-interface basis. |
Interface Trust Mode |
Specifies whether or not an interface (or all interfaces if the Slot/Port field is set to Global) trust a particular packet marking when the packet enters the port. The default value is trust dot1p. The mode can only be one of the following:
|
Non-IP Traffic Class |
This field appears if the trust mode for the selected interface is trust ip-precedence or trust ip-dscp. The field displays the traffic class (queue) to which all non-IP traffic is directed when in the interface trust mode is trust ip-precedence or trust ip-dscp. The valid range is 0 to 6. |
Untrusted Traffic Class |
This field appears if the trust mode for the selected interface is untrusted. The field displays the traffic class (queue) to which all traffic is directed when in untrusted mode. The valid range is 0 to 6. |
Current 802.1p Priority Mapping |
Displays the current 802.1p priority mapping configuration. |
The Trust Mode Configuration page also displays the Current 802.1p Priority Mapping table.
Use the IP DSCP Mapping Configuration page to map an IP DSCP value to an internal traffic class. To display the IP DSCP Mapping Configuration page, click Quality of Service > Class of Service > IP DSCP Mapping Configuration in the navigation menu.
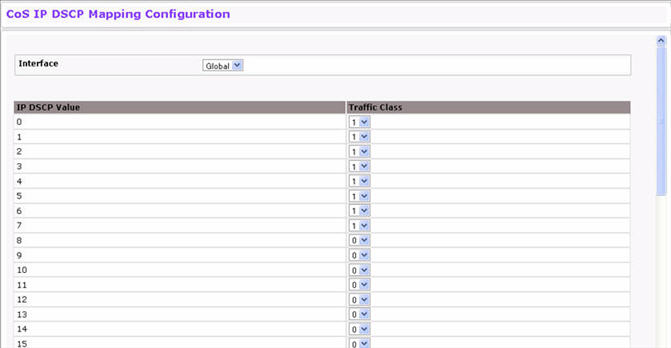
IP DSCP Mapping Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface/Global |
The menu contains all CoS configurable interfaces. The only option is Global, which means that the IP DSCP mapping configuration applies to all interfaces and cannot be applied on a per-interface basis. |
IP DSCP Values |
Lists the IP DSCP values to which you can map an internal traffic class. The values range from 0-63. |
Traffic Class |
The traffic class is the hardware queue for a port. Higher traffic class values indicate a higher queue position. Before traffic in a lower queue is sent, it must wait for traffic in higher queues to be sent. Valid range is 0 to 7. |
Use the Interface Configuration page to apply an interface shaping rate to all ports or to a specific port. To display the Interface Configuration page, click Quality of Service > Class of Service > Interface Configuration in the navigation menu.
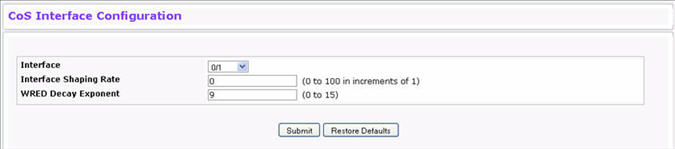
Interface Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface/Global |
Selects the CoS configurable interface to be affected by the Interface Shaping Rate. Select Global to apply a rate to all interfaces. Select an individual port to override the global setting. |
Interface Shaping Rate |
Sets the limit on how much traffic can leave a port. The limit on maximum transmission bandwidth has the effect of smoothing temporary traffic bursts over time so that the transmitted traffic rate is bounded. The specified value represents a percentage of the maximum negotiated bandwidth. The default value is zero (0). Valid values are 0-100, in increments of 1. A value of 0 means the maximum is unlimited. |
WRED Decay Exponent |
Specifies the decay exponent value used with the WRED average queue length calculation algorithm. Default value is 9. Valid Range is (0 to 15). |
If you make changes to the page, click Submit to apply the changes to the system. Click Restore Defaults to reset all interfaces to the default trust value.
Use the Interface Queue Configuration page to define what a particular queue does by configuring switch egress queues. User-configurable parameters control the amount of bandwidth used by the queue, the queue depth during times of congestion, and the scheduling of packet transmission from the set of all queues on a port. Each port has its own CoS queue-related configuration.
The configuration process is simplified by allowing each CoS queue parameter to be configured globally or per-port. A global configuration change is automatically applied to all ports in the system. To display the Interface Queue Configuration page, click Quality of Service > Class of Service > Interface Queue Configuration in the navigation menu.
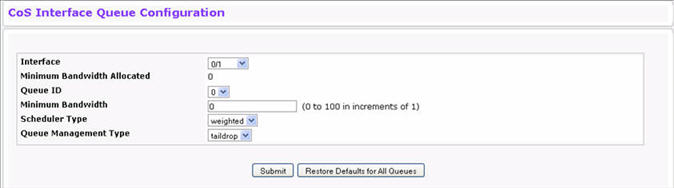
Interface Queue Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface/Global |
Specifies the interface (physical, LAG, or Global) to configure. |
Minimum Bandwidth Allocated |
Shows the sum of individual Minimum Bandwidth values for all queues in the interface. The sum cannot exceed the defined maximum of 100. This value is considered while configuring the Minimum Bandwidth for a queue in the selected interface. |
Queue ID |
Use the menu to select the queue per interface to be configured. |
Minimum Bandwidth |
Specify the minimum guaranteed bandwidth allocated to the selected queue on the interface. Setting this value higher than its corresponding Maximum Bandwidth automatically increases the maximum to the same value. The default value is 0. The valid range is 0 to 100, in increments of 1. The value zero (0) means no guaranteed minimum. The sum of individual Minimum Bandwidth values for all queues in the selected interface cannot exceed defined maximum 100. |
Scheduler Type |
Selects the type of queue processing from the dropdown menu. Options are Weighted and Strict. Defining on a per-queue basis allows the user to create the desired service characteristics for different types of traffic.
|
Queue Management Type |
Displays the type of queue depth management techniques used for all queues on this interface. This is only used if the device supports independent settings per-queue. Queue Management Type can only be Taildrop. The default value is Taildrop. All packets on a queue are safe until congestion occurs. At this point, any additional packets queued are dropped. |
Use the Interface Queue Status page to view CoS queue interface queue configuration information for each interface. To display the Interface Queue Status page, click Quality of Service > Class of Service > Interface Queue Status in the navigation menu.
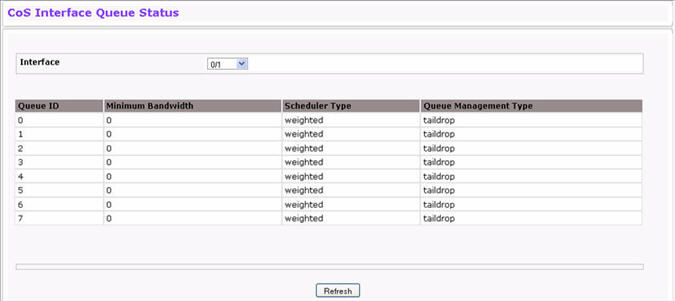
Interface Queue Status Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface/Global |
Select the CoS configurable interface with the queue status information to display. The option Global represents the most recent global configuration settings. These may be overridden on a per-interface basis. |
Queue ID |
Lists the queues for the interface. |
Minimum Bandwidth |
Shows the minimum guaranteed bandwidth allotted to this queue on the interface. A value of zero (0) means no guaranteed minimum. The sum of individual Minimum Bandwidth values for all queues in the selected interface cannot exceed the defined maximum of 100. |
Scheduler Type |
Shows the type of scheduling used for this queue. The available options are as follows:
|
Queue Management Type |
Displays the queue depth management technique used for queues on this interface, which can only be Taildrop. This is only used if the device supports independent settings per-queue. All packets on a queue are safe until congestion occurs. At this point, any additional packets queued are dropped. |
Click Refresh to update the information on the screen.
Use the Interface Queue Drop Precedence Configuration page to configure thresholds for packet loss during times of queue congestion. Each port can have its own drop precedence configuration or all ports can be globally configured.
To display the Interface Queue Drop Precedence Configuration page, click Quality of Service > Class of Service > Interface Queue Drop Precedence Configuration in the navigation menu.
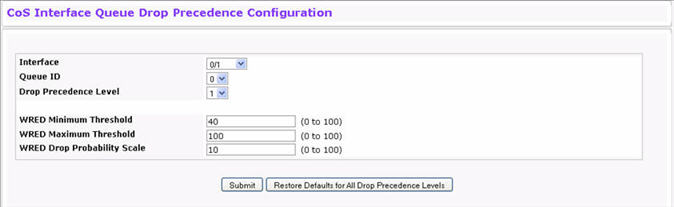
Interface Queue Drop Precedence Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface/Global |
Specify the interface (physical, LAG, or Global) to configure. |
Queue ID |
Select a queue to associate with the interface to be configured. |
Drop Precedence Level |
Select a drop precedence levels (platform-based). |
WRED Minimum Threshold |
Specify the weighted RED minimum queue threshold below which no packets are dropped for the current drop precedence level. Default values are:
|
WRED Maximum Threshold |
Specify the weighted RED maximum queue threshold above which all packets are dropped for the current drop precedence level. Default values are:
|
WRED Drop Probability |
Specify the packet drop probability for the current drop precedence level. Default value is 10. Valid Range is (0 to 100). |
Use the Interface Queue Status page to view interface queue drop precedence configuration information for the CoS queues for each interface. To display the Interface Queue Drop Precedence Status page, click Quality of Service > Class of Service > Interface Queue Drop Precedence Status in the navigation menu.
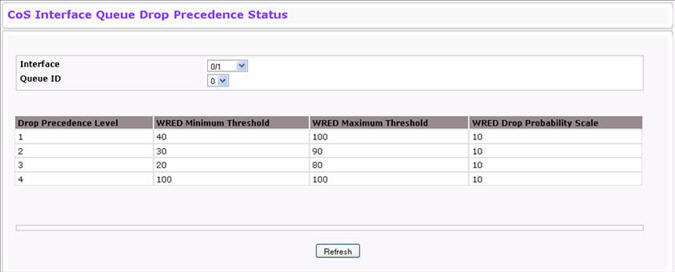
Click Refresh to update the information on the screen.