TejNOS-EN software supports the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP). SNTP assures accurate network device clock time synchronization up to the millisecond. Time synchronization is performed by a network SNTP server. TejNOS-EN software operates only as an SNTP client and cannot provide time services to other systems.
Time sources are established by Stratums. Stratums define the accuracy of the reference clock. The higher the stratum (where zero is the highest), the more accurate the clock. The device receives time from stratum 1 and above since it is itself a stratum 2 device.
The following is an example of stratums:
Information received from SNTP servers is evaluated based on the time level and server type.
SNTP time definitions are assessed and determined by the following time levels:
The device can poll Unicast and Broadcast server types for the server time.
Polling for Unicast information is used for polling a server for which the IP address is known. SNTP servers that have been configured on the device are the only ones that are polled for synchronization information. T1 through T4 are used to determine server time. This is the preferred method for synchronizing device time because it is the most secure method. If this method is selected, SNTP information is accepted only from SNTP servers defined on the device using the SNTP Server Configuration page.
Broadcast information is used when the server IP address is unknown. When a Broadcast message is sent from an SNTP server, the SNTP client listens to the message. If Broadcast polling is enabled, any synchronization information is accepted, even if it has not been requested by the device. This is the least secure method.
The device retrieves synchronization information, either by actively requesting information or at every poll interval. If Unicast and Broadcast polling are enabled, the information is retrieved in this order:
MD5 (Message Digest 5) Authentication safeguards device synchronization paths to SNTP servers. MD5 is an algorithm that produces a 128‐bit hash. MD5 is a variation of MD4, and increases MD4 security. MD5 verifies the integrity of the communication, authenticates the origin of the communication.
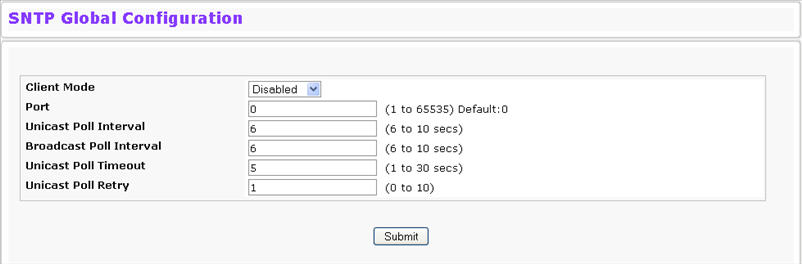
Use the SNTP Global Configuration page to view and adjust SNTP parameters.
To display the SNTP Global Configuration page, click System > SNTP > Global Configuration in the navigation menu.
SNTP Global Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Client Mode |
Use drop‐down list specify the SNTP client mode, which is one of the following modes:
|
Port |
Specifies the local UDP port to listen for responses/broadcasts. Allowed range is (1 to 65535). Default value is 0. |
Unicast Poll Interval |
Specifies the number of seconds between unicast poll requests expressed as a power of two when configured in unicast mode. Allowed range is (6 to 10). Default value is 6. |
Broadcast Poll Interval |
Specifies the number of seconds between broadcast poll requests expressed as a power of two when configured in broadcast mode. Broadcasts received prior to the expiry of this interval are discarded. Allowed range is (6 to 10). Default value is 6. |
Unicast Poll Timeout |
Specifies the number of seconds to wait for an SNTP response when configured in unicast mode. Allowed range is (1 to 30). Default value is 5. |
Unicast Poll Retry |
Specifies the number of times to retry a request to an SNTP server after the first time‐out before attempting to use the next configured server when configured in unicast mode. Allowed range is (0 to 10). Default value is 1. |
If you change any of the settings on the page, click Submit to apply the changes to system.
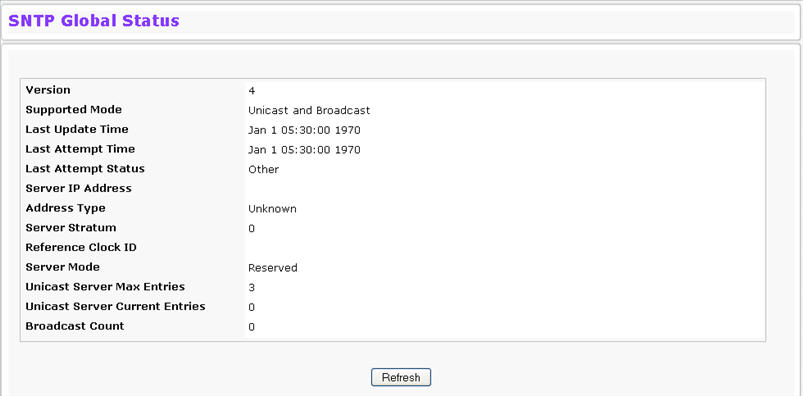
Use the SNTP Global Status page to view information about the system’s SNTP client. To access the SNTP Global Status page, click System > SNTP > Global Status in the navigation menu.
Global Status Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Version |
Specifies the SNTP Version the client supports. |
Supported Mode |
Specifies the SNTP modes the client supports. Multiple modes may be supported by a client. |
Last Update Time |
Specifies the local date and time (UTC) the SNTP client last updated the system clock. |
Last Attempt Time |
Specifies the local date and time (UTC) of the last SNTP request or receipt of an unsolicited message |
Last Attempt Status |
Specifies the status of the last SNTP request or unsolicited message for both unicast and broadcast modes. If no message has been received from a server, a status of Other is displayed. These values are appropriate for all operational modes:
|
Server IP Address |
Specifies the IP address of the server for the last received valid packet. If no message has been received from any server, an empty string is shown. |
Address Type |
Specifies the address type of the SNTP Server address for the last received valid packet. |
Server Stratum |
Specifies the claimed stratum of the server for the last received valid packet. |
Reference Clock Id |
Specifies the reference clock identifier of the server for the last received valid packet. |
Server Mode |
Specifies the mode of the server for the last received valid packet. |
Unicast Sever Max Entries |
Specifies the maximum number of unicast server entries that can be configured on this client. |
Unicast Server Current Entries |
Specifies the number of current valid unicast server entries configured for this client. |
Broadcast Count |
Specifies the number of unsolicited broadcast SNTP messages that have been received and processed by the SNTP client since last reboot. |
Click Refresh to display the latest information from the router.
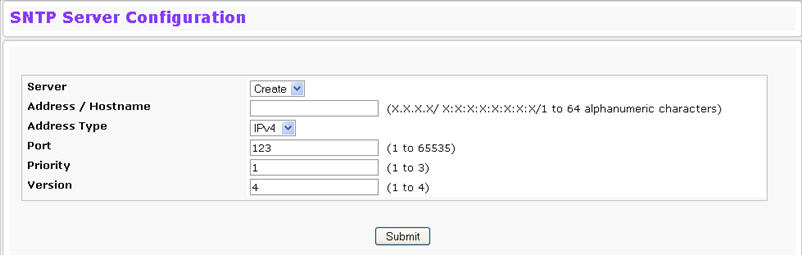
Use the SNTP Server Configuration page to view and modify information for adding and modifying Simple Network Time Protocol SNTP servers. To display the SNTP Server Configuration page, click System > SNTP > Server Configuration in the navigation menu.
SNTP Server Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Server |
Select the IP address of a user‐defined SNTP server to view or modify information about an SNTP server, or select Create to configure a new SNTP server. You can define up to three SNTP servers. |
Address / Hostname |
Enter the IP address or the hostname of the SNTP server. |
Address Type |
Select IPv4 if you entered an IPv4 address, IPv6 if you entered an IPv6 address or DNS if you entered a hostname. |
Port |
Enter a port number from 1 to 65535. The default is 123. |
Priority |
Enter a priority from 1 to 3, with 1 being the highest priority. The switch will attempt to use the highest priority server and, if it is not available, will use the next highest server. |
Version |
Enter the protocol version number. |
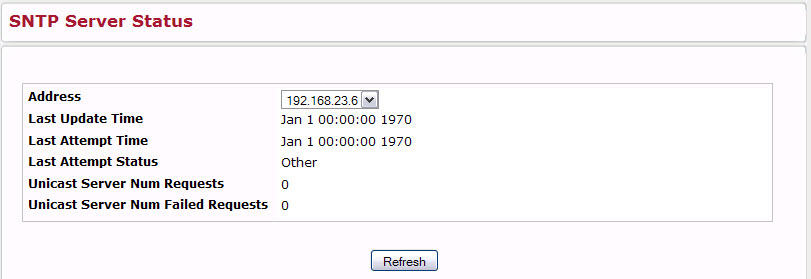
The SNTP Server Status page displays status information about the SNTP servers configured on your switch. To access the SNTP Server Status page, click System > SNTP > Server Status in the navigation menu.
SNTP Server Status Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Address |
Specifies all the existing Server Addresses. If no Server configuration exists, a message saying “No SNTP server exists” flashes on the screen. |
Last Update Time |
Specifies the local date and time (UTC) that the response from this server was used to update the system clock. |
Last Attempt Time |
Specifies the local date and time (UTC) that this SNTP server was last queried. |
Last Attempt Status |
Specifies the status of the last SNTP request to this server. If no packet has been received from this server, a status of Other is displayed:
|
Unicast Server Num Requests |
Specifies the number of SNTP requests made to this server since last agent reboot. |
Unicast Server Num Failed Requests |
Specifies the number of failed SNTP requests made to this server since last reboot. |
Click Refresh to display the latest information from the switch.