sFlow® is the standard for monitoring high‐speed switched and routed networks. sFlow technology is built into network equipment and gives complete visibility into network activity, enabling effective management and control of network resources.
The sFlow monitoring system consists of an sFlow Agent (embedded in a switch or router or in a standalone probe) and a central sFlow Collector. The sFlow Agent uses sampling technology to capture traffic statistics from the device it is monitoring. sFlow datagrams are used to immediately forward the sampled traffic statistics to an sFlow Collector for analysis.
The sFlow Agent uses two forms of sampling: statistical packet‐based sampling of switched or routed Packet Flows, and time‐based sampling of counters.
Packet Flow Sampling and Counter Sampling are performed by sFlow Instances associated with individual Data Sources within the sFlow Agent. Packet Flow Sampling and Counter Sampling are designed as part of an integrated system. Both types of samples are combined in sFlow datagrams. Packet Flow Sampling will cause a steady, but random, stream of sFlow datagrams to be sent to the sFlow Collector. Counter samples may be taken opportunistically in order to fill these datagrams.
In order to perform Packet Flow Sampling, an sFlow Sampler Instance is configured with a Sampling Rate. The Packet Flow sampling process results in the generation of Packet Flow Records. In order to perform Counter Sampling, the sFlow Poller Instance is configured with a Polling Interval, The Counter Sampling process results in the generation of Counter Records. The sFlow Agent collects Counter Records and Packet Flow Records and sends them in the form of sFlow datagrams to sFlow Collectors.
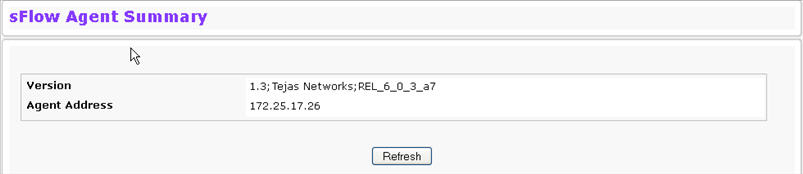
To access the sFlow Agent Summary page, click System > sFlow > Agent Summary in the navigation menu.
sFlow Agent Summary
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Version |
Uniquely identifies the version and implementation of this MIB. The version string must have the following structure: MIB Version;Organization;Software Revision where:
|
Agent Address |
The IP address associated with this agent. |
Use the Refresh button to refresh the page with the most current data from the switch.
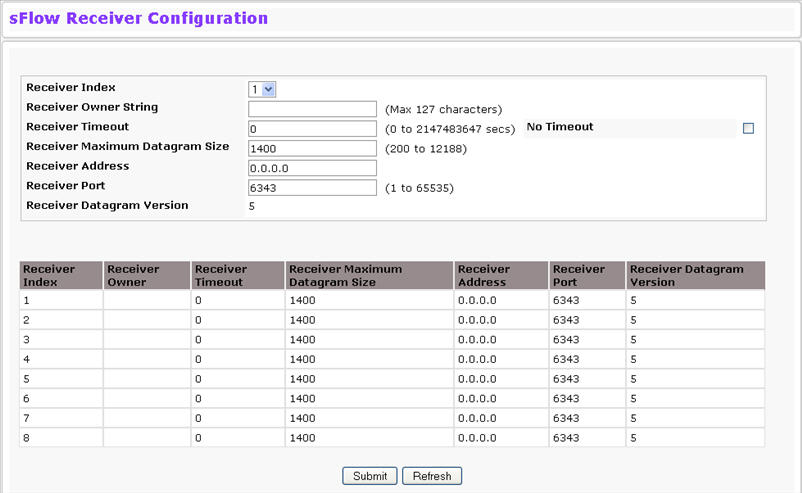
Use the sFlow Receiver Configuration page to configure the sFlow Receiver. To access the sFlow Receiver Configuration page,
sFlow Receiver Configuration
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Receiver Index |
Selects the receiver for which data is to be displayed or configured. The allowed range is 1 to 8. |
Receiver Owner String |
The entity making use of this sFlowRcvrTable entry. The empty string indicates that the entry is currently unclaimed and the receiver configuration is reset to the default values. An entity wishing to claim an sFlowRcvrTable entry must ensure that the entry is unclaimed before trying to claim it. The entry is claimed by setting the owner string. The entry must be claimed before any changes can be made to other sampler objects. |
Receiver Timeout |
The time (in seconds) remaining before the sampler is released and stops sampling. A management entity wanting to maintain control of the sampler is responsible for setting a new value before the old one expires. The allowed range is 0 to 2147483647 seconds. A value of zero sets the selected receiver configuration to its default values. |
No Timeout |
Select this option to set the timeout value to a non‐decrementing value of 2147483647 seconds for a receiver. The receiver entry is deleted from the configuration only after timeout value is zero, so by selecting the No Timeout option, the specified entry remains in the configuration until you explicitly remove the entry. |
Receiver Maximum Datagram Size |
The maximum number of data bytes that can be sent in a single sample datagram. The manager should set this value to avoid fragmentation of the sFlow datagrams. The default value is 1400. The allowed range is 200 to 12188.) |
Receiver Address |
The IP address of the sFlow collector. If set to 0.0.0.0 no sFlow datagrams will be sent. |
Receiver Port |
The destination port for sFlow datagrams. The allowed range is 1 to 65535). |
Receiver Datagram Version |
The version of sFlow datagrams that should be sent. |
The sFlow agent collects time‐based sampling of network interface statistics and sends them to the configured sFlow receivers. A data source configured to collect counter samples is called a poller.
Counter Sampling
The primary objective of Counter Sampling is to efficiently, periodically export counters associated with Data Sources. A maximum Sampling Interval is assigned to each sFlow instance associated with a Data Source.
Counter Sampling is accomplished as follows:
The sFlow Agent keeps a list of counter sources being sampled. When a Packet Flow Sample is generated, the sFlow Agent examines the list and adds counters to the sample datagram, least recently sampled first. Counters are only added to the datagram if the sources are within a short period of failing to meet the required Sampling Interval. Periodically, every second, the sFlow Agent examines the list of counter sources and sends any counters that need to be sent to meet the sampling interval requirement.
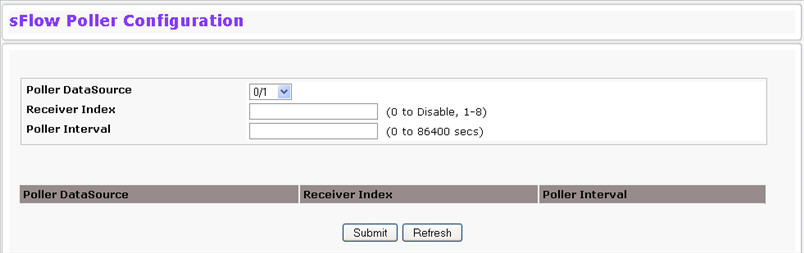
To access the sFlow Poller Configuration page,
sFlow Poller Configuration
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Poller DataSource |
The sFlow Sampler Datasource for this flow sampler. This Agent will support Physical ports only. |
Receiver Index |
The sFlowReceiver for this sFlow Counter Poller. If set to zero, the poller configuration is set to the default and the poller is deleted. Only active receivers can be set. If a receiver expires, then all pollers associated with the receiver will also expire. The allowed range is 1 to 8. |
Poller Interval |
The maximum number of seconds between successive samples of the counters associated with this data source |
The sFlow Agent collects a statistical packet‐based sampling of the switched flows and sends them to the configured receivers. A data source configured to collect flow samples is called a sampler.
Packet Flow Sampling
The Packet Flow Sampling mechanism carried out by each sFlow instance ensures that any packet observed at a Data Source has an equal chance of being sampled, irrespective of the Packet Flow(s) to which it belongs.
Packet Flow Sampling is accomplished as follows:
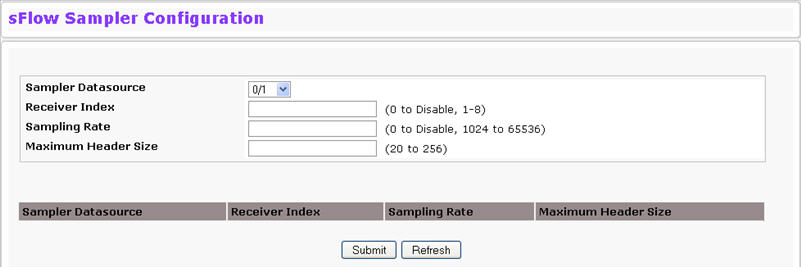
To access the sFlow Sampler Configuration page, click System > sFlow > Sampler Configuration in the navigation menu.
sFlow Sampler Configuration
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Poller DataSource |
The sFlow Datasource for this sFlow sampler. This Agent will support Physical ports only. |
Receiver Index |
The sFlow Receiver for this sFlow sampler. If set to zero, no packets will be sampled. Only active receivers can be set. If a receiver expires, then all samplers associated with the receiver will also expire. The allowed range is 1 to 8. |
Sampling Rate |
The statistical sampling rate for packet sampling from this source. A sampling rate of one (1) counts all packets. A sampling rate of zero (0) disables sampling. The allowed range is 1024 to 65536. |
Maximum Header Size |
The maximum number of bytes that should be copied from a sampled packet. The allowed range is 20 to 256. |