If a packet is untagged or priority- tagged, the device associates the packet with any matching IP subnet classification. If no IP subnet classification can be made, the packet is subjected to the normal VLAN classification rules of the device. An IP subnet-to-VLAN mapping is defined by configuring an entry in the IP subnet-to-VLAN table. An entry is specified by a source IP address, network mask, and the desired VLAN ID. The IP subnet-to-VLAN configurations are shared across all ports of the switch.
Use the IP Subnet-based VLAN Configuration page to assign an IP Subnet to a VLAN. To display the IP Subnet-based VLAN Configuration page, click Switching > IP Subnet-based VLAN > Configuration in the navigation menu.
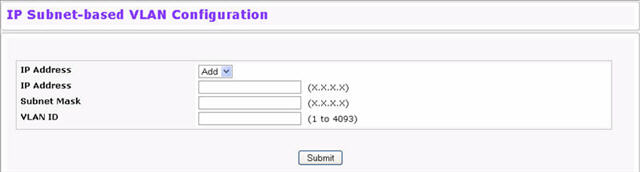
IP Subnet-based VLAN Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
IP Address |
Select the IP address of the IP-to-VLAN binding to view or delete, or select Add to create a new binding. |
IP Address |
Specifies packet source IP address. This field is configurable only when you create a new IP Subnet-based VLAN. Enter the IP address in dotted decimal notation. |
Subnet Mask |
Specifies packet source IP subnet mask address.This field is configurable only when you create a new IP Subnet-based VLAN. Enter the subnet mask in dotted decimal notation. |
VLAN ID |
Specifies the VLAN to which the IP address is assigned. The valid range is 1-3965. |
Use the IP Subnet-based VLAN Summary page to view information about IP subnet to VLAN mappings configured on your system. If no mappings are configured, the screen displays a “No IP Subnet-based VLAN Configured” message. To access the IP Subnet-based VLAN Summary page, click Switching > IP Subnet-based VLAN Summary in the navigation menu.
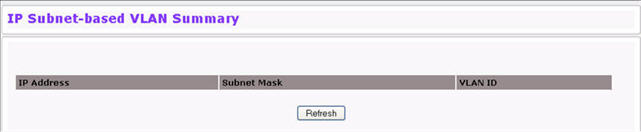
IP Subnet-based VLAN Summary Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
IP Address |
Shows the packet source IP address. |
Subnet Mask |
Shows packet source IP subnet mask address. |
VLAN ID |
Shows the VLAN to which the IP address is assigned. |
Click Refresh to reload the page and display the most current information.