The voice VLAN feature enables switch ports to carry voice traffic with defined settings so that voice and data traffic are separated when coming onto the port. A voice VLAN ensures that the sound quality of an IP phone is safeguarded from deterioration when data traffic on the port is high.
The inherent isolation provided by VLANs ensures that inter-VLAN traffic is under management control and that network-attached clients cannot initiate a direct attack on voice components. A QoS protocol based on the IEEE 802.1P class-of-service (CoS) protocol uses classification and scheduling to send network traffic from the switch in a predictable manner. The system uses the source MAC of the traffic traveling through the port to identify the IP phone data flow.
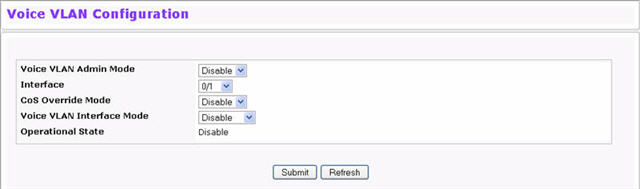
Voice VLAN is enabled per-port basis. A port can participate only in one voice VLAN at a time. The Voice VLAN feature is disabled by default. To display the Voice VLAN Configuration page, click System > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Configuration.
Voice VLAN Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Voice VLAN Admin Mode |
Click Enable or Disable to administratively turn the Voice VLAN feature on or off for all ports. |
Interface |
Select the interface to configure this service on. |
CoS Override Mode |
Overrides the 802.1p class-of-service (CoS) value for all data (non-voice) packets arriving at the port. Thus any rogue client that is also connected to the voice VLAN port cannot deteriorate the voice traffic. |
Voice VLAN Interface Mode |
Select one of the following interface modes:
|
Operational State |
Indicates whether the voice VLAN is operational. |