You can configure the switch to use IEEE 802.1ad (Dot1ad) provider bridging functionality. Dot1ad enables customers to maintain their own VLANs inside a service provider's VLAN.
NOTE: The Dot1ad feature is available in the optional Metro package.
Dot1ad builds upon the IEEE 802.1Q specification, which defined how 801.Q VLAN tags can be encapsulated within Ethernet frames in a second layer of 802.1Q tags (802.1Q-in-Q). The second layer of tags enables service providers to identify and forward a customer’s VLAN traffic while it traverses the provider network to multiple customer sites - ensuring separation from other customers’ data, even when their networks use the same primary VLAN identifiers. The second layer of tags may also be used to enable particular layer-2 protocols to be tunneled through the provider network to multiple customer sites. This is referred to as layer-2 protocol tunneling.
To enable a VLAN on the switch to be bridged throughout the service provider network, you define service instances. A service instance definition includes the service name and S-VID (service VLAN ID) and the type of forwarding to use.
The administrator can subscribe individual ports to a service. When a port subscribes to a service, a unique service VLAN (identified by the service S-VID) is created on the switch (if it does not already exist) and the subscribing port is configured as a participant in the SVLAN. The service provider port (called the Network-to-Network, or NNI, port) is also configured as a participant in the SVLAN in order to transmit and receive upstream/downstream traffic.
A subscription includes match criteria such as the customer VLAN ID (C-VID), priority, and S-VID. When an incoming packet on uni-p matches the criteria on the port, the switch adds the service VLAN tag to the packet and optionally remarks the C-VID/removes the C-tag before forwarding/redirecting to the service provider network. When an incoming packet on uni-s matches the criteria on the port, the switch may remark S-VID and/or remarks C-VID/removes C-tag to the packet before forwarding/redirecting to the service provider network.
When the incoming packet on NNI matches the criteria, the switch performs a combination of the following:
Each UNI port PVID is set to the TLS service VLAN ID for which the port is subscribed. None of the other service-subscriptions on the port affect the PVID of the port. The PVID of the NNI port is set to the Management VLAN. The default management VLAN is 1). Creation and participation behavior of VLANs on the switch is the same for all types of services (TLS, E-LAN, E-TREE, E-LINE) of services.
To enable a switch port to perform protocol tunneling to a remote site, you specify a reserved MAC, Protocol ID, and VLAN ID (S-VID) that identify the protocol to be tunneled, and the action that the local port should take when protocol data units (PDUs) of that protocol type are received.
In order to participate in service subscriptions and Dot1ad protocol tunneling, a switch port must be configured to be either a:
A service instance definition names the service and describes how it operates. The service is uniquely identified by service VLAN Id (S-VID). After you create a service instance, you can subscribe a switch port to the service and configure the criteria for determining which network traffic is associated with that service.
To create a service instance, click Switching > DOT1ad > Service Configuration.
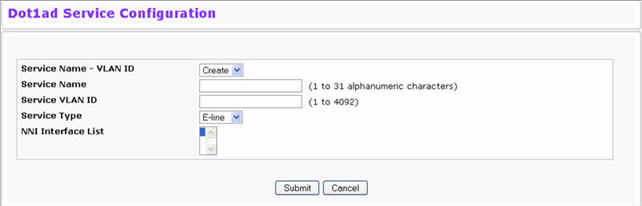
Dot1ad Service Configuration
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Service Name - VLAN ID |
To create a new Dot1ad service, select the Create option from the menu. To view information about or to delete an existing service, select the name of the service from the list. |
Service Name |
The user-assigned name of the service. |
Service VLAN ID |
The service VLAN ID (S-VID). |
Service Type |
These parameters define the type of traffic associated with this service instance. E-LINE - The e-line parameter creates a point-to-point service, in which traffic is forwarded directly to the WAN port in the upstream direction and to the associated user port in the downstream direction. An e-line service type bypasses the standard VLAN/MAC based switching decision. Up to 4K service can be subscribed. E-LAN is a service-instance that can be applied to multiple user ports. It can be point-to-multipoint (E-LAN) or multipoint-to-multipoint:
ETREE - Creates a point-to-multi-point service, in which the traffic associated with that service is forwarded direct to the NNI port in the upstream direction and direct to the associated UNI port(s) in the downstream direction. If an E-TREE service-instance is applied to multiple UNI ports it becomes a point-to-multipoint service in which the participating user ports are still isolated from each other. NOTE: Downstream broadcast, multicast and unknown destination (DLF) traffic is still forwarded (replicated) to all UNI ports participating in the E-TREE service. TLS (Transparent LAN Service) functions as a default service type for unknown service traffic on a port. If a port does not subscribe to any TLS service instance, all packets not matching any of the service instances configured on the port are dropped. If a port subscribes to a TLS service instance, unknown service traffic is mapped to the TLS and forwarded to the WAN port(s). |
NNI Interface List |
List of NNI Interfaces associated with the Dot1ad service. |
To view a summary of all existing services,
If you have defined a service instance on the switch, you can subscribe ports to that service. To subscribe a port to a service, you associate the service with the port number and define match criteria for packets received on the interface. When a packet matches the criteria, the port performs a combination of the following (based on the subscription configurations on the UNI ports):
To use the Web Interface to create or modify a subscription, click Switching > DOT1ad > Subscription Configuration. Initially, when no subscriptions have been configured, the page displays as follows.
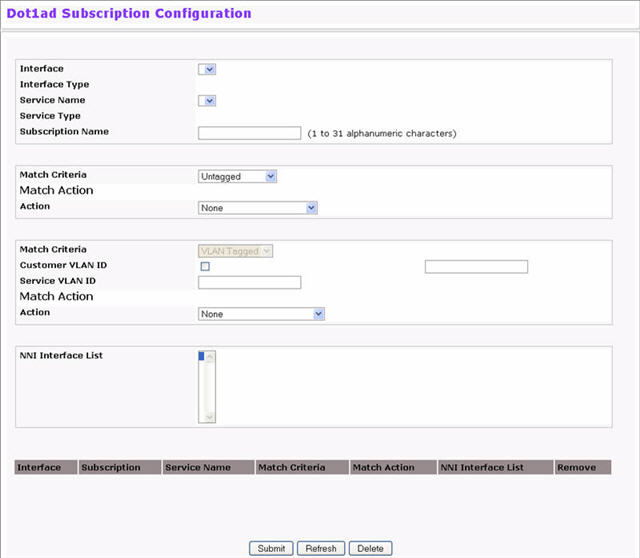
Dot1ad Subscription Configuration
Field |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
Interface |
Select the interface to configure. |
|
Interface Type |
Shows the dot1ad interface type
|
|
Service Name |
Select a service from the list to associate with the selected port. |
|
Service Type |
Shows the type of dot1ad service. |
|
Subscription Name |
Enter a name assigned to this subscription. |
|
Match Criteria |
Select the match criteria. Packets that match this criteria are associated with the service and are subjected to the action selected in the Action field.
|
|
Customer VLAN ID |
The C-VID value that must be matched in order for the service to be associated and the specified action to be taken on the packet. This field is only editable when VLAN Tagged is selected as the Match Criteria. |
|
Service VLAN ID |
Service VLAN ID of a tagged packet to be matched. |
|
Priority |
The priority value that must be matched in order for the service to be associated and the specified action to be taken on the packet. This field is only editable when VLAN Tagged is selected as the Match Criteria. |
|
Match Action Fields |
||
Action |
The action to be taken when the match criteria is satisfied:
|
|
Customer VLAN ID |
The C-VID to assign to packets that match the criteria. |
|
NNI Interface List |
List of NNI Interfaces to be associated with this subscription. NOTE: This is applicable for E-Line services only (where the same S-VID is shared for different subscriptions). |
|
A summary of the subscription configuration for the interface displays at the bottom of the page.
To view a summary of all current subscriptions,
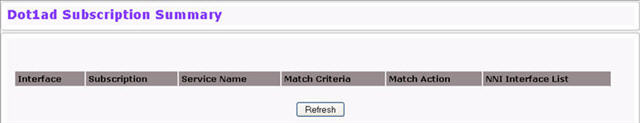
To use service subscriptions and L2 protocol tunneling, you must identify the ports involved as:
An NNI port expects incoming packets to be tagged with a S-VID. When an untagged packet is received on an NNI port, it is terminated by default. When an S-tagged packet is received on an NNI port, it performs a combination of the following and forwards/redirects the packet to the appropriate UNI port(s):
Only a UNI port can be configured to tunnel PDUs of a particular protocol ID and destination MAC address or to add an S-VID to a packet based on service match criteria. When a UNI port receives a PDU that matches the criteria, the UNI tags the PDU in a combination of the following ways (based on subscriptions action criteria) and forwards/redirects it to the NNI port(s):
To use the Web Interface to set the dot1ad interface type, click Switching > DOT1ad > Interface Type Configuration.
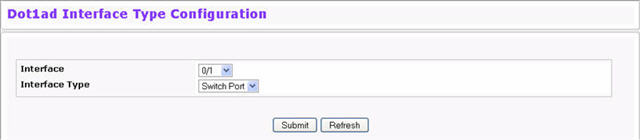
Dot1ad Interface Type Configuration
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface |
Select the interface to configure a tunnel on. |
Interface Type |
Select UNI-P for a User-to-Network port-based interface. Select UNI-S for a User-to-Network service-based interface. Select NNI if the port serves as an interface to the core service-provider network. |
To view the Dot1ad Interface Type Summary, click Switching > DOT1ad > Interface Type Summary.
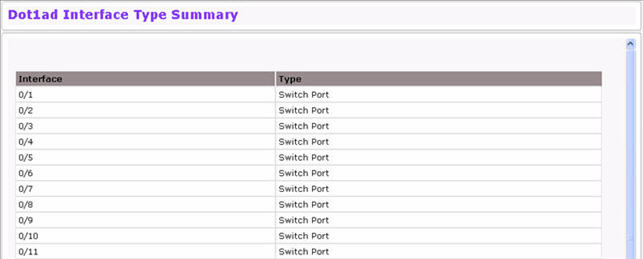
The page lists each port and UNI/NNI type.
Click Refresh to redisplay the page with the latest data from the switch.
Customers at different sites connected across a service-provider network may want to run various layer 2 protocols to scale their topology across all their local and remote sites. This allows them to treat their geographically dispersed network as a single layer 2 network. The switch enables tunneling layer 2 protocols across the service provider network, by encapsulating the layer 2 protocol packets with a service VLAN (S-VLAN) tag as they are forwarded to the service-provider network.
To configure L2 protocol tunneling on an interface, you specify it as 802.1ad network-to-network interface (NNI) or user-to-network interface (UNI).
Use the Protocol Tunnel Configuration page to configure the action (tunnel, terminate, discard, or discard-shutdown) the interface takes when it receives a PDU with a specified combination of reserved MAC address, protocol ID, and VLAN ID. If a UNI interface is configured to tunnel the protocol/MAC address PDUs, the switch tags the PDUs appropriately and forwards them to the NNI port(s).
To use the Web Interface to configure a port to perform L2 protocol tunneling,
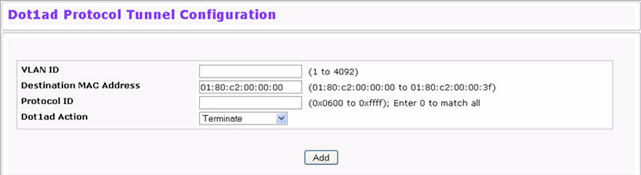
Tunnel Action Configuration
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
VLAN ID |
Select the VLAN to configure a tunnel on. |
Destination MAC Address |
Enter the MAC address. The allowed address range is from 01:80:C2:00:00:00 to 01:80:C2:00:00:3F. |
Protocol ID |
Enter the protocol ID. The allowed protocol ID range is a hexadecimal value from 0x0001 to 0xFFFF. The combination of the protocol-id and MAC-address value is matched against any incoming PDUs to determine whether the configured action is taken. |
Dot1ad Action |
Select the action to be taken when a packet’s protocol ID and destination MAC address match the criteria. Options are:
|
To view a list of all configured tunnels and the actions they take on matching packets,