The Priority-based Flow Control (PFC) feature allows the user to pause (inhibit transmission) of individual priorities within a single physical link. By configuring PFC to independently pause congested priorities, protocols that are highly loss sensitive can share the same link with traffic with different loss tolerances. Priorities are differentiated by the priority field of the 802.1Q VLAN header.
PFC uses a control packet defined in 802.1Qbb and is not compatible with 802.3x FC. When PFC is disabled on an interface, the FC configuration for the interface becomes active. FC frames received on a PFC configured interface are ignored.
Each priority is configured as either drop or no-drop. When a priority that is designated as no-drop becomes congested, the priority is paused. Drop priorities do not participate in pause.
PFC is disabled by default (there are no priority classifications configured).
NOTE: Support for this feature is platform-dependent.
 CAUTION: All ports may be briefly shutdown when modifying either Flow Control (FC) or PFC settings.
CAUTION: All ports may be briefly shutdown when modifying either Flow Control (FC) or PFC settings.
To enable priority-based flow control for a particular CoS value on an interface:
An interface that is configured for PFC is automatically disabled for 802.3x Flow Control. When priority-based flow control is enabled, the interface will not pause any CoS unless there is at least one no-drop priority. When PFC is disabled, the interface defaults to the IEEE 802.3x flow control setting for the interface.
To display the PFC Configuration page, click Switching > PFC > PFC Configuration in the navigation menu.
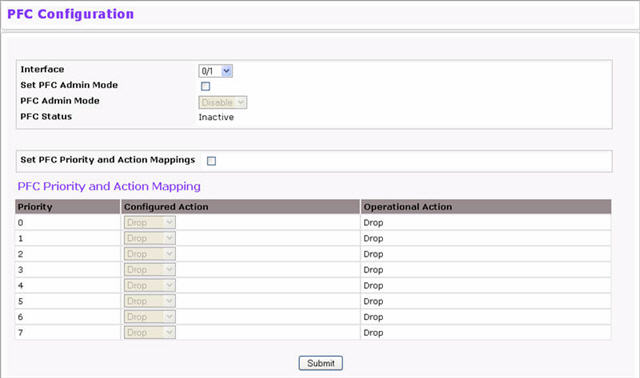
PFC Configuration Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface |
Select the Unit/Port or LAG from drop-down menus for PFC treatment. Click Global to specify all interfaces. |
Set PFC Admin Mode |
Select to enable the ability to configure the Admin Mode, then select Enable or Disable from the PFC Admin Mode field. |
PFC Admin Mode |
Sets the Admin Mode to enable or disable PFC on the selected interface. |
PFC Status |
Displays the operational status (Active/Inactive) of PFC on the selected interface. |
Set PDC Priority and Action Mappings |
Select to enable the ability to assign an action to each priority level. |
Action |
Select the action (Drop/No-Drop) to be applied for the corresponding Priority value on the selected interface. |
Click Submit to save any configuration changes.
Use the PFC Statistics page to view the PFC statistics for interfaces on the switch. To display the PFC Statistics page, click Switching > PFC > PFC Statistics in the navigation menu.
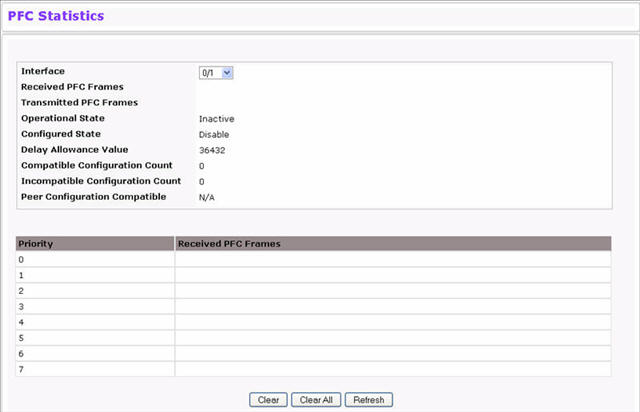
PFC Statistics
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Interface |
Select the interface for which to display statistics. |
Received PFC Frames |
Displays the total number of PFC frames that have been received by selected interface. |
Transmitted PFC Frames |
Displays the total number of PFC frames that have been received by the selected interface. |
Priority |
Displays the priority value of which the PFC statistics of the selected interface are being shown. |
Received PFC Frames (per Priority) |
Displays the number of PFC frames that have been received by this interface for this priority. |